
|
| |||||||
| Protein Homology/analogY Recognition Engine V 2.2 | ||||||||
|

|
| |||||||
| Protein Homology/analogY Recognition Engine V 2.2 | ||||||||
|
When to run Intensive mode - example |
| This example illustrates when you might want to
run an intensive job after examining the results from a normal
mode.
The really important thing to remember is
that running an intensive job is normally a really
bad idea.
Note that the top hit that Phyre2 gives details for is the same solution as hit no. 1 in the list of (up to) 20 that are actually modelled.
|
Normal mode result and analysis |
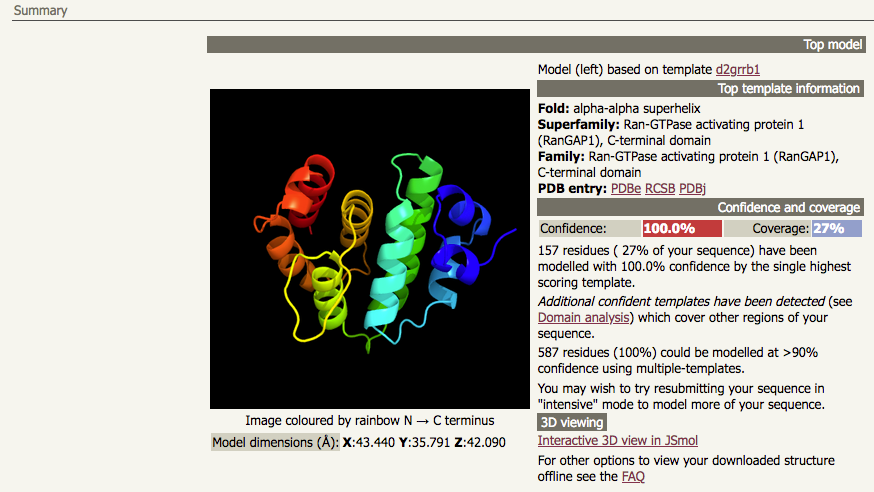
| A normal mode job for the UniProt accession P46060 (which has 587 amino acids) will give a top hit with high confidence and high sequence identity, but with low coverage: |
|
|
In this particular case, the output from the normal mode job tells you that running intensive mode may be a good idea. There is additional information that supports this suggestion. The first thing to note is that the "top hit" result has 100% confidence but only 27% coverage, indicating that there is 73% of the sequence which has not been modelled. Immediately below that output, Phyre2 tells you that
|
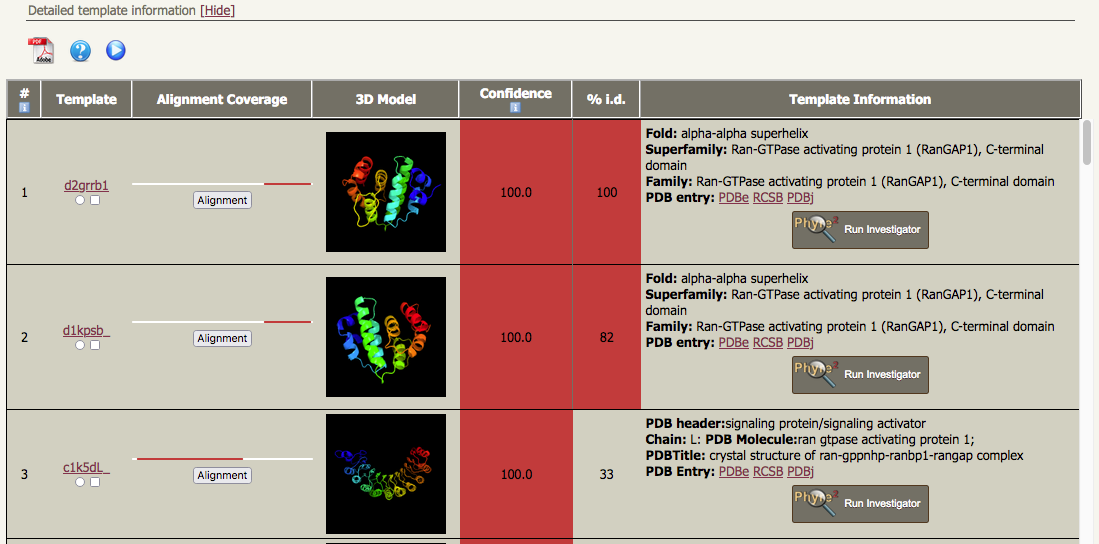
| In addition to this, if you look at the "Detailed template information", there are two quite different well-ordered models in the list of results, each of which covers a large proportion of the sequence. The first two models in the list correspond to alpha-alpha superhelices from the C-terminal domains from RanGAP1 proteins, but the third Phyre2 model is an alpha-beta solenoid (or a right-handed beta-alpha superhelix) composed of a leucine-rich repeat region. |
|
|
The Phyre2 template for hit no. 1 is "d2grrb1";
Hit no. 3 corresponds to the template library entry c1k5dL_, i.e. it's based on chain L from PDB entry 1k5d. Apart from this having a completely different fold to hits 1 and 2, note that the confidence of this model is also 100%, but the % ID is only 33%. Checking the Alignment Coverage bar charts (to the left of the ribbon diagrams) it can be seen that the red bars for hits 1 and 2 broadly overlap with each other (~residues 431 - 587) but not with that for hit 3 (22-361). Taken together, we would like to be able to knit the two different parts together and that is precisely what intensive mode tries to do. There is one important caveat to be borne in mind. The template library has no information about the linkage between these two templates or about the relative orientation between them, so any model produced from intensive mode that includes both templates is very highly speculative.
|
Intensive mode contra-indications |
|
The message that "You may wish to try resubmitting your sequence in "intensive" mode" is insufficient on its own to justify running intensive mode. Even when you get this message, there are several pointers that indicate that running it will not give additional useful information. For example;
These are all indicators that it is very unlikely that Intensive mode will help.
|
Intensive mode result and analysis |
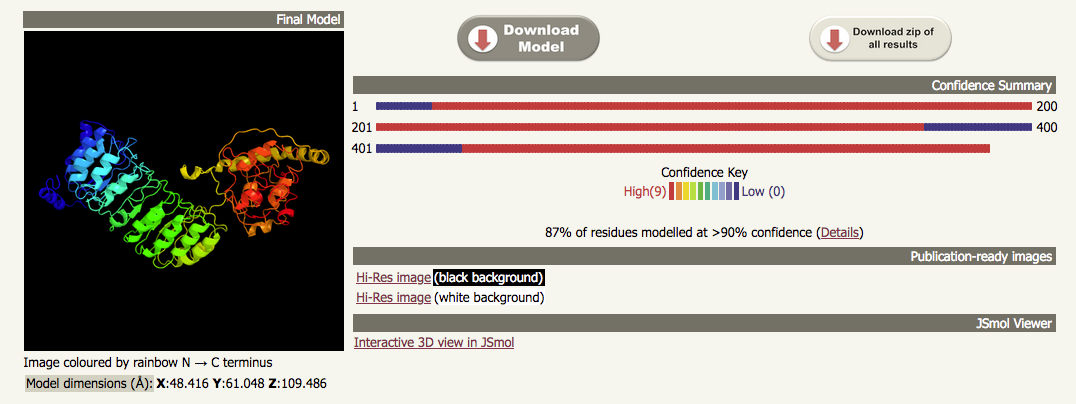
| If we look at the top of the output from the intensive job run using the same sequence, we can see that the ribbon diagram shows a model that has been built using the models from templates 1 and 3 from the normal mode run. The output on the right of the ribbon diagram has been replaced with some that shows how much of the sequence has been modelled by each of the two templates; in this case, 87% of the sequence has been modelled with > 90% confidence. |
|
A note on Intensive mode and AlphaFold |
|
Observant readers will have noticed that the linked page for
UniProt accession P46060 includes a
reference to the model produced by
AlphaFold
(at the time of writing there are ~220,000,000
AlphaFold models available). It's interesting to note that,
while the two individual domains predicted by Phyre2 and
Alphafold are broadly similar, their mutual orientation is
somewhat different.
As noted above, the linking performed by Phyre2 intensive mode is not very reliable - but the linkage in the Alphafold model is also unreliable; the residues concerned are predicted with "very low" confidence, and the PAE matrix plot shows that the spatial relationship of the two domains is speculative. It is likely that, while both results may be useful, neither should be taken to represent the true complete 3D structure. |
Phyre is now FREE for commercial users!
All images and data generated by Phyre2 are free to use in any publication with acknowledgement
Accessibility Statement| Please cite: Phyre2.2: A Community Resource for Template-based Protein Structure Prediction | |||||||||
| Powell HR et al. Journal of Molecular Biology (2025) in press DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2025.168960 | |||||||||
|
 |
|
|||||||